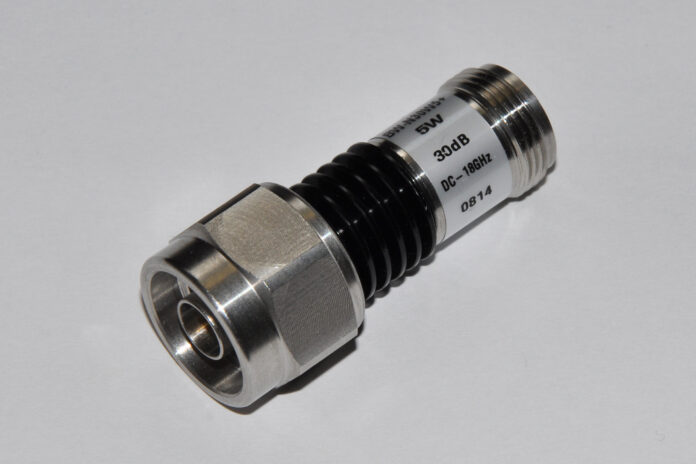
Variable and fixed attenuators can both come in handy & do their purpose for your everyday electricity tools and help with the circuit. You can also get the right model and use it or apply it in your line of work, as long as it works and is suitable for your initial placement. However, they function differently and have different perks, pros & cons, which is why it is crucial to understand the basics, but also the key difference among the two. Keep on reading as we discuss and talk about the most important and main components that you should know about attenuators.
7 Things to know about Variable and Fixed Attenuators
1. What is an attenuator?

To start it off slow & easy, you should first know what this item is. Attenuators are electrical components designed to reduce the amplitude of a signal passing through the component.
They can do this with ease and without making an impact on the signal thanks to their RF application. There are six different kinds of attenuator options, and those are fixed, step, programmable, dc bias, and dc blocking, as well as variable. In this article, we will focus on and talk about fixed and variable kinds.
2. All about fixed kinds
Fixed Attenuators are waveguide components that you can use and enjoy their particular attenuation value into the waveguide network for signal leveling or reflection compensation. These are, as the name itself says fixed, meaning that they can’t be changed once set up. Their configuration can be either the L, Tee, or Pi kind. Attenuators typically consist of a resistive network that allows heat to dissipate at a certain rate. Fixed attenuators are set at a fixed and unchanging component and feature by these resistive networks. Once placed down and applied the model can be directional or bidirectional. It is used in industries where true precision & fixed rates are needed for tools & their function.
3. Variable model kinds

Continuously variable kinds can be adjusted per your preference and wish in a manual way to get the right specified range and resolution for your use. They are variable since they can change and you can make a physical manual impact on them. The voltage applied to the device controls the attenuation of voltage variable attenuators. Voltage variable attenuators are employed in various electronic circuits to reduce the input power from a source to a predetermined value that is suitable for a specific load. There are either linear or non-linearized variables that are used for the voltage-to-attenuation transfer feature. Variable models are more so used in industries where true precision by the nearest mm is not needed.
4. Their design & looks
An attenuator is a simple passive tool that has a two-port passage for an electronic circuit that is built using passive components also known as resistors. It is a simple & small-looking item. The looks and the design of this model can vary and change based on several elements, such as balance & directory that are needed. In most cases, here is what to expect and how the models look like:
- They have PIN diodes
- Loads of sections per request, as well as your needed features
- Can be designed using FET RF attenuators
- Sturdy and is well-built
Their main feature and connection is the analog control voltage for controlling the attenuation levels.
5. Different kinds

As previously mentioned & explained, there are loads of different kinds & circuit layout options, such as pi, T, L, H, and O configurations. All are mainly different in their looks & configuration system. You can classify and arrange these through their circuit levels, symmetrical balance options, or configurations that are needed for the end result and the end product. Some are already pre-made and ready to sell, while some may need to be specifically ordered. The mechanical construction of a waveguide variable attenuator may be critical, for some applications. Most models are limited with their RF microwave power, which is why there is a wide range of different variable power levels in the system.
6. Use in networking
In the communication systems and the communication industry, both kinds & models are more than welcome and needed. Some industries prefer fixed kinds while others will enjoy variable models for their use in the industry. This is because the signals are transmitted from one point to another. If signals are transmitted over long distances then there will be some reduction in their strength or even slower performance. Their use is nowadays applied in most industries, for computer & data networking, as well as for telegram & radio signals.
7. Their application

Lastly, if you’re wondering where to apply these two kinds or if they differ in any way, here is what to expect and where annunciators can come in handy on a daily or in your line of work:
Through the help of PIN diode, you can control the microwave power with your attenuator
Control the volume of electronic equipment such as speakers, electric guitars, etc
- In laboratories of different kinds
- For high-powerful radio frequencies
- In some digital or analog circuits
- For optic communication
- For telecommunication
Where to find the right model?
In the end, do you feel like you’ve learned a lot regarding these two? Well, in conclusion, both models are used to adjust power, reduce reflection interaction, and provide isolation where needed. Wondering why use it, how to choose the best model, or if fixed or variable options are for you? At Custom Microwave every user will easily find and work with their needed pattern & model. Browse through their spec sheets or flange sheets and look at your options. Choose the right part name, look at its WR & GHz frequency, while also getting the right length. Attenuators come in sizes from WR3 to WR42 with hole patterns that will suit your personal at-home or professional use. Give them a click and make a change!