Understanding the impact of wind load on buildings is crucial for architects, engineers, and builders. This 450-word blog post delves into the complexities of calculating wind load, providing expert tips and techniques to ensure structural safety and compliance with building codes. Our guide is designed to be accessible to a diverse readership, making complex information digestible for all.
Fundamentals of Calculating Wind Load
Understanding the Basics

Calculating wind load involves understanding several key factors, including wind speed, the shape and height of the building, and the surrounding terrain. An engineer often employs the basic formula for load calculation, which is P = qz * G * Cp – qi * (GCpi), where each variable represents a specific aspect of the building and its environment. This formula is a fundamental tool in the arsenal of wind calculations engineers, enabling them to accurately assess and mitigate the impacts of wind on various structures.
Tools and Techniques
Several tools and techniques are used in the calculation. This includes tunnel testing, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and the use of specific software designed for structural analysis. These tools help in providing a more accurate assessment a building might face.
Advanced Considerations
Impact of Building Shape and Surrounding Terrain
The shape of a building and the surrounding terrain play a significant role in how it affects a structure. Tall, slender buildings are more susceptible to loads compared to lower, more robust structures. The terrain, whether urban, suburban, or rural, also affects wind speed and direction.
Adhering to Building Codes and Standards
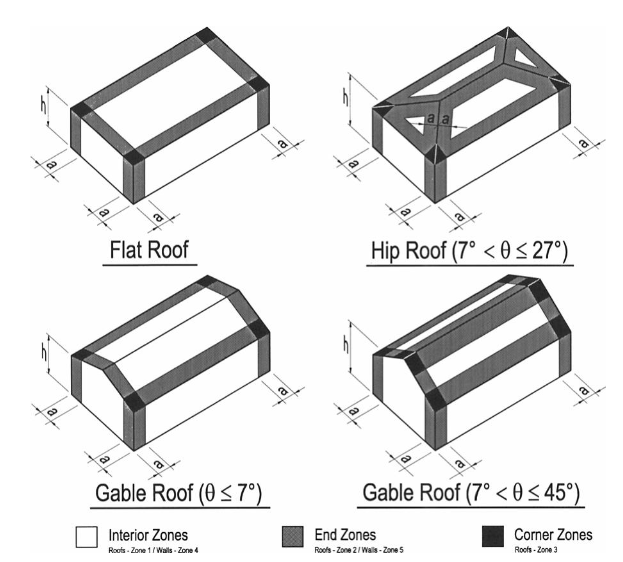
Adhering to building codes and standards is essential in calculation and overall structural design. These regulations are established based on extensive research and historical data, ensuring that buildings can withstand local environmental conditions, including wind forces. They vary by region, reflecting the specific climatic and geographical challenges of each area.
Compliance with these codes is not just a legal obligation but a crucial aspect of ensuring public safety and structural integrity. Engineers and architects must be well-versed in these standards to design buildings that are not only safe and durable but also cost-effective. Regular updates to these codes also mean professionals must stay informed about the latest changes to maintain the highest standards of building safety.
Innovations in Analysis
Emerging Technologies and Methods
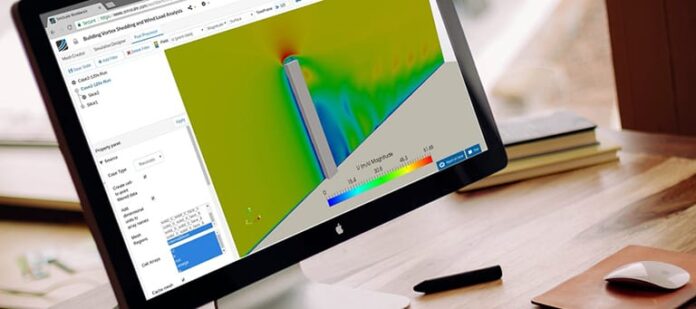
Recent advancements in technology have significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of analysis. Innovations like advanced computational models and enhanced wind tunnel testing allow for more precise simulations of wind behavior. These advancements lead to better predictions of how wind interacts with various building shapes and materials, enabling safer and more cost-effective designs.
The Role of Sustainability in Design
Sustainability in building design is not just about energy efficiency and material choice; it also involves the resilience of a structure against natural forces like wind. Sustainable designs often incorporate features that naturally mitigate wind loads such as aerodynamic shapes and flexible materials. These eco-friendly designs not only reduce the environmental impact but also enhance the building’s ability to withstand high winds.
Conclusion
Calculating wind load on buildings is a complex but essential part of architectural and engineering work. By understanding the fundamentals and utilizing advanced tools and techniques, professionals can design structures that are both safe and compliant with necessary standards. This guide provides a starting point for those looking to deepen their understanding of wind load calculations.