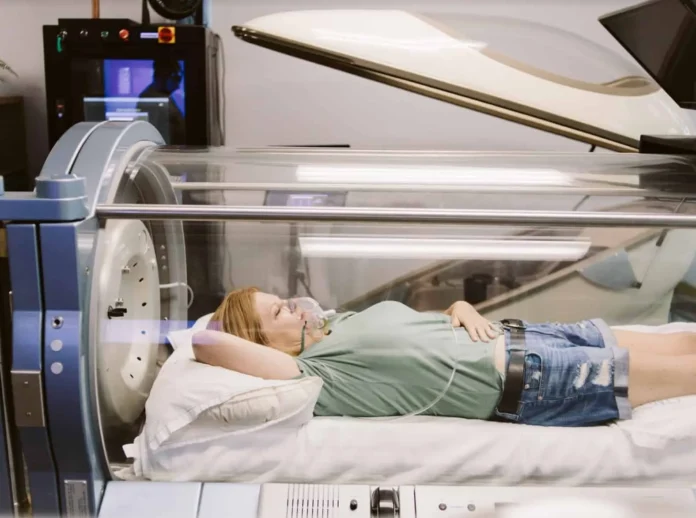
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment that involves breathing in pure oxygen while inside a pressurized chamber. HBOT has been used to treat a variety of medical conditions, including decompression sickness, wounds that won’t heal, and carbon monoxide poisoning. In recent years, there has been growing interest in the potential benefits of HBOT for immune system health. Here, we will explore the link between hyperbaric oxygen therapy and immune system health.
Understanding the Immune System

The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body against infections and diseases. The immune system is made up of two main components: the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system. The innate immune system provides immediate, non-specific defense against foreign invaders, while the adaptive immune system targets specific pathogens and creates long-term immunity. If you want to learn more about this amazing therapy, you should visit oxyhelp.com.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy and Immune System Health
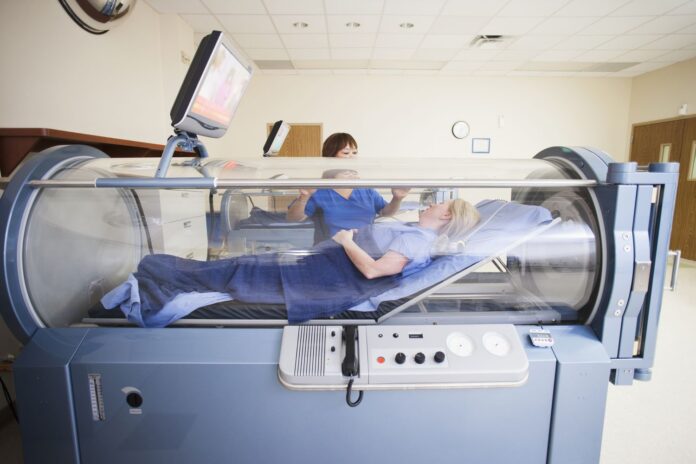
HBOT is thought to support immune system health by increasing oxygen levels in the body, which can stimulate the immune system’s response to infections and diseases. HBOT has been shown to increase the production of white blood cells, which play a crucial role in the immune system’s defense against pathogens.
HBOT has also been shown to increase the production of nitric oxide, a molecule that helps regulate immune function. Nitric oxide has been shown to have antimicrobial properties and may play a role in regulating inflammation in the body.
In addition, HBOT may support immune system health by improving the oxygenation of tissues and organs. This can help improve the function of immune cells and may enhance the body’s ability to fight off infections and diseases.
Research on Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy and Immune System Health

While there is some evidence to suggest that HBOT may support immune system health, more research is needed to fully understand the link between HBOT and immune system function.
One study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology found that HBOT increased the production of white blood cells in rats. Another study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery found that HBOT improved the survival rate of rats infected with deadly bacteria.
A study published in the journal PLOS ONE found that HBOT increased the production of nitric oxide in human subjects. However, more research is needed to determine whether this increase in nitric oxide translates to improved immune function.
Conclusion
While the link between HBOT and immune system health is not yet fully understood, there is growing evidence to suggest that HBOT may have potential benefits for immune system function. HBOT has been shown to increase the production of white blood cells, improve the production of nitric oxide, and enhance the oxygenation of tissues and organs. Further research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits of HBOT for immune system health, but these early findings are promising.