The joints in your body are the points at which bones meet. Joints include your hips, knees, knuckles, elbows, and shoulders. The vertebrae also possess joints. Tendons, ligaments, synovial fluid, and cartilage are some of the tissues found in a joint. They assist you in moving and give support.
Illness or injury to the joints can obstruct your mobility and create a great deal of discomfort that can result in long-lasting pain. Joint pain is characterized by pain and tenderness in any of the joints. Joint discomfort affects a large number of people. It can result from a number of sources. Because of the many causes, the symptoms, treatments, and outcomes vary. The most prevalent types of joint pain are listed here, along with the generally accepted therapies for each, as well as the types of doctors that treat or specialize in each.
1. Arthritis
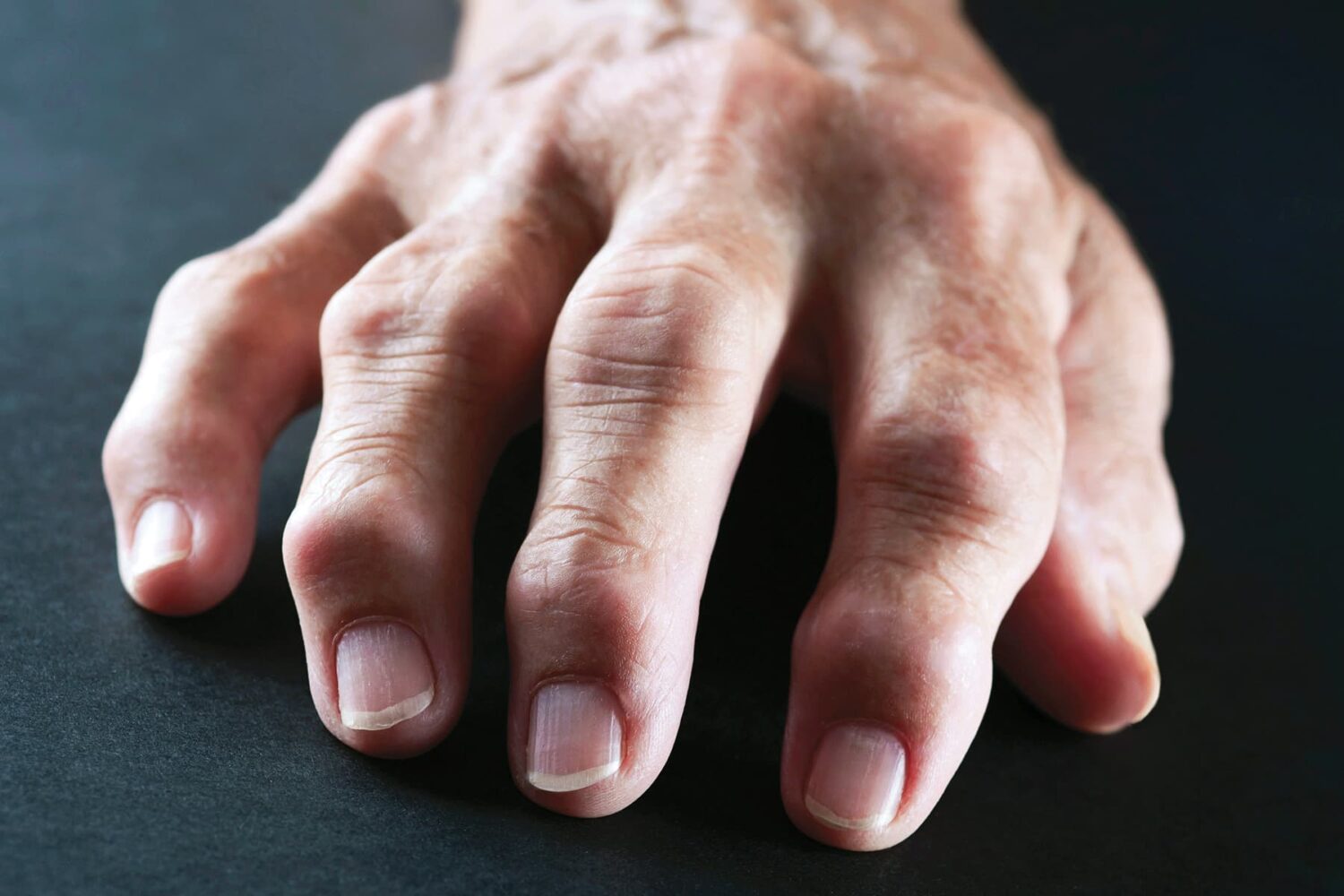
This is a type of joint swelling that generates discomfort and redness in the joints. It can damage the muscle tissue, but it greatly impacts the joints. Arthralgia is the medical term for the joint pain caused by this. Polyarthritis is a type of arthritis in which multiple joints are affected. Oligoarthritis is a type of arthritis that affects two or three joints. Monoarthritis is a type of arthritis that affects just one joint.
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis. Gout and rheumatoid arthritis are two more frequent rheumatic disorders linked to arthritis. The pathophysiology of the illness process frequently results in articular cartilage degeneration as well as ankylosis. Inflammation of the lungs can be caused by rheumatoid arthritis.
Accepted treatments for arthritis
Although there is no permanent remedy for arthritis, a variety of treatments can help to relieve symptoms and/or slow the progression of the condition. Your doctor can prescribe a variety of treatments to help you manage pain, avoid joint injuries, and reduce swelling. Medication, Occupational Therapy, surgical joint replacement, exercise, and joint protection are all examples of this.
The medications you take will be determined by the type of arthritis you have. Higher vitamin D consumption was linked to a lower incidence of RA. As a result, the doctor may prescribe vitamin D-rich medication. Analgesics, which relieve pain, are common medications that may be recommended for you. NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications) are pain relievers that also reduce inflammation.
Another treatment that has been suggested is occupational therapy. Where do you exercise your affected area? Use braces to protect particular joints and avoid postures that pressure your joints. Rheumatologists are doctors who specialize in the nonsurgical management of arthritis. They are frequently consulted to help assess and treat a patient’s arthritis treatment plan.
2. Overuse injuries from repetitive motion
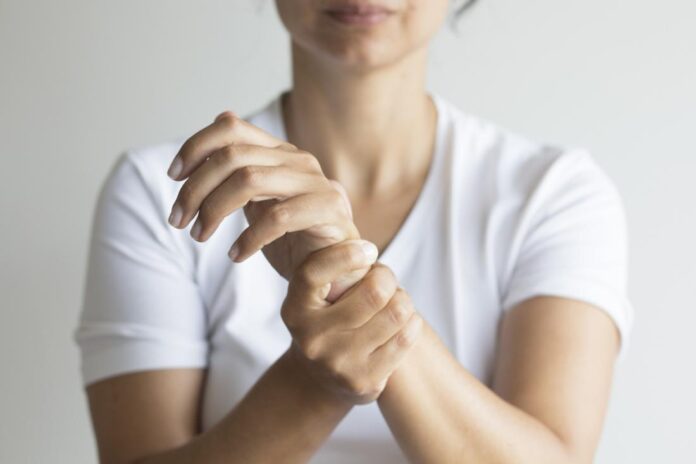

Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is a broad term for the discomfort experienced by repetitive actions and strains in muscles, ligaments, and joints. The illness mostly impacts the upper body, particularly parts of the hands, neck, and shoulders.
RSIs are frequent and can be caused by a variety of activities, such as repetitive motions, performing a high-intensity task for an extended period of time without rest, poor posture, or occupations that require working in an uncomfortable position. RSI can be caused by jobs that require repeated motions, which include working on a production line, at a grocery store, or on a computer.
Treatment of repetitive strain injuries
It’s advisable to contact your doctor about RSI if you’re having even slight discomfort performing particular chores at work or at home. Identifying and modifying the work or activity that is generating the symptoms is generally the first step in treating RSI. You may have to cease the action completely if required.
The therapy for RSI discomfort is initially moderate. RICE, which stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation, may be used, as well as steroid injections, wrapping the region or fastening it with a bandage to cushion and relax the ligaments and joints. Your doctor may recommend non-steroidal anti-swelling medicines such as ibuprofen or paracetamol. A physiotherapist may be recommended to you for postural advice as well as advice on how to improve or ease your joints.
3. Sport-related injuries
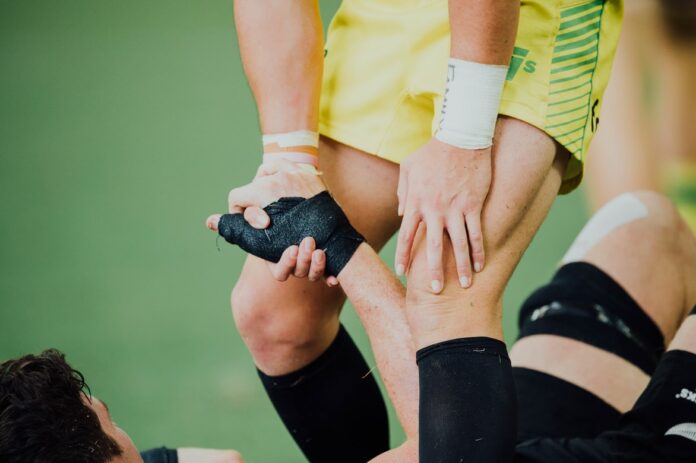

The muscular system is damaged mostly by sports injuries, either suddenly or gradually. Wrestling, rock climbing, and jogging are examples of high-impact sports or activities that need repetitive action. Dislocations, sprains, and strains have all been linked to activities that cause joint discomfort, either directly or indirectly.
A sprain occurs when a ligament is stretched or torn. They keep the bones in your joints together. Ankle injuries, knee sprains, and wrist sprains are all common sprains. When an excessive amount of stress is applied to a ligament, the ends of two linked bones separate, causing a dislocation. Joint ligament pressure can make the joint dislocate, over extending it and potentially tearing the joints and/or ligaments
Treatment of sports-related injuries
Usually, small sports injuries may be treated at home by resting the afflicted body part and taking over-the-counter pain relievers. Major injuries may prompt surgery in order to correct or fix the affected joints.
Therapeutic exercise and treatment are two procedures used to describe active rehabilitation. It is a customized program that combines rest, exercise, and physiotherapy to expedite the restoration of normal function and prevent competitors and sportspeople from losing fitness while resting the injured portion.
Typically an orthopedist, like Dr. Bryan Gruber at Integrated Orthopedics, would be the specialist you would need to see to help treat these types of injuries depending on their severity.
4. Rheumatic disorders
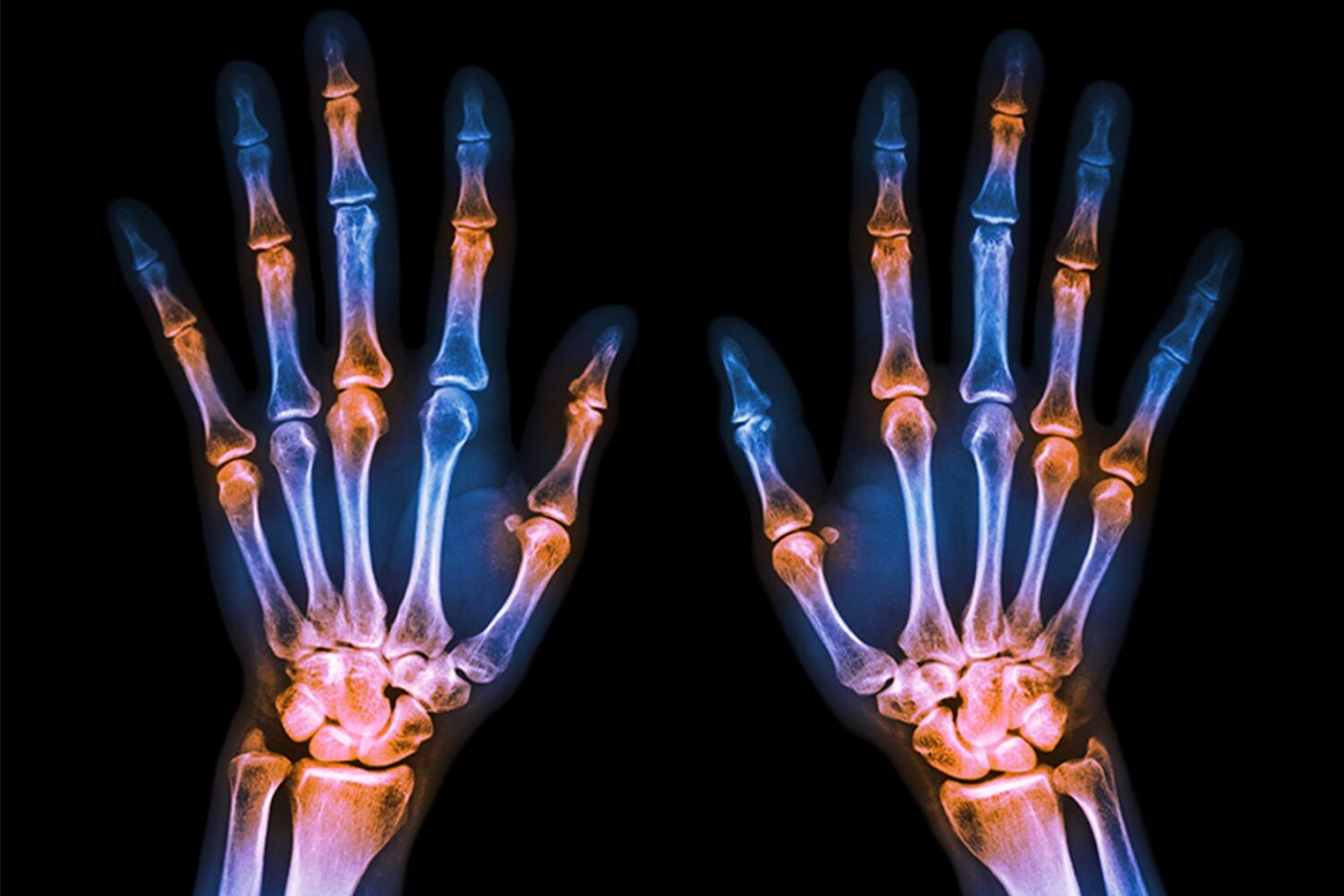
Inflammatory illnesses affect the joints, bones, and organs by causing your immune system to fight them. Lupus and spondyloarthritis are two of the most frequent rheumatic illnesses.
Lupus is a disease in which the immune system assaults its own cells and organs, triggering joint as well as organ dysfunction. Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, as well as fever and exhaustion, are the most prevalent indications and symptoms. It can be caused by genetics, environmental factors such as sun exposure, viral diseases, tiredness, distress, and anything else that puts the body under physical stress.
Treatment of Lupus
For instance, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory inhibitor drugs can be used to treat people with mild lupus who have minor joint discomfort. The antimalarial medicine hydroxychloroquine, which affects the immune system, is another treatment that can be used to manage Lupus. A rheumatologist is a specialist that specializes in joint and muscle illnesses like lupus.
5. Spondyloarthritis
Spondyloarthritis is a term used to describe a group of inflammatory illnesses that damage the joints in the vertebrae and soft tissue, as well as other parts of your body. Some examples of this inflammatory condition are ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. Spondyloarthritis is difficult to diagnose, especially because it can manifest itself in a variety of ways. The rigidity and symptoms of spondyloarthritis, on the other hand, appear to be more profound in the early morning or after extended immobility.
Treating Spondyloarthritis
Most treatment suggestions recommend starting with an NSAID, but depending on the conditions, the practitioner may decide to start with a biologic drug.
6. Osteoporosis
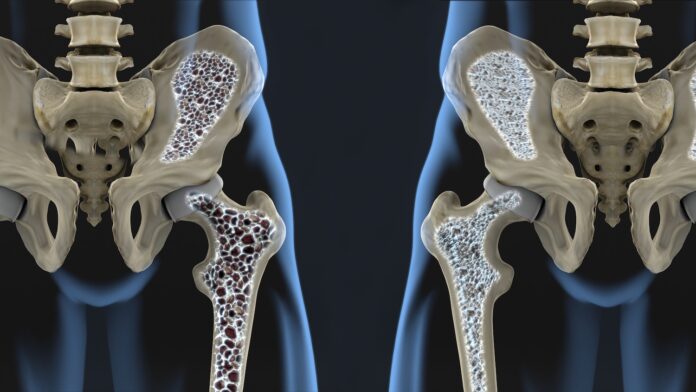
It’s a bone-weakening illness that puts you at a higher risk for unanticipated fractures if you do have it. Osteoporosis is defined as the loss of bone strength and size. The condition frequently progresses without causing any signs of discomfort, and it isn’t detected until the weakening bones result in severe fractures. The majority of them have wrist as well as spine fractures.
Treatment of Osteoporosis
Workouts, vitamins, and medicines may be used to treat developed osteoporosis. Exercise and supplements are frequently recommended to aid in the prevention of osteoporosis. The importance of muscle mass, resistance, and balancing exercises cannot be overstated.