The market offers a wide variety of linear motion products, making it challenging to choose the right one. This article examines the different types of products based on their rolling element and discusses their benefits and drawbacks. It is important for an individual to understand the unique features of each product, so he can make a good decision in selecting the best linear motion product.
Some of the linear motion products are:
- Linear Bearings, Housings, Shafts & Supports
- Heavy Duty Rollers (NUTR, NUKR, NNTR)
- Vee Bearings
- Motion Guidance Systems (Standard & Aluminium)
- Miniature Motion Guidance
- Track Guidance System
- Combined Roller Bearings
- Plain Sliding Linear Bearings
What do Linear Motion Products Represent?
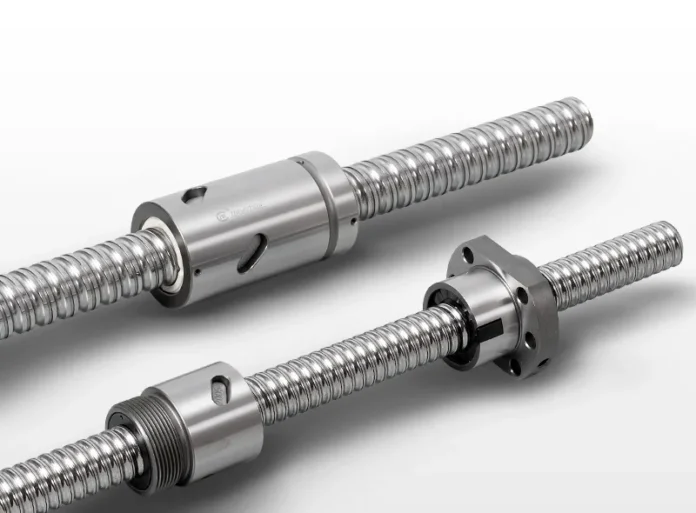

Linear motion products are designed to move objects in a single direction along a straight line. This is often achieved using bearings that have a rolling element, such as a ball or roller. However, there are now “plain” bearings available that do not have a rolling element and instead use plastic or ceramic bushes. These bushes may also be lined with PTFE or oil-impregnated plastic to reduce sliding friction.
It is achievable to have linear motion without using bearings, but it requires more effort to move a load without them. Bearings can significantly reduce friction, with a recirculating ball bushing having a coefficient of friction as low as 0.001. In comparison, steel against steel with lubrication has a coefficient of friction of 0.10.
There are different ways to move linear bearings, such as using screws, belts, chains, racks, pinions, or manual force. These bearings can also be combined with other linear motion products to create multi-directional systems with either two or three axes. Some examples of these systems include an XY table with two axes or a CNC machine with three axes.
Variety of Different Products to Know About and Their Benefits
1. Linear bearings
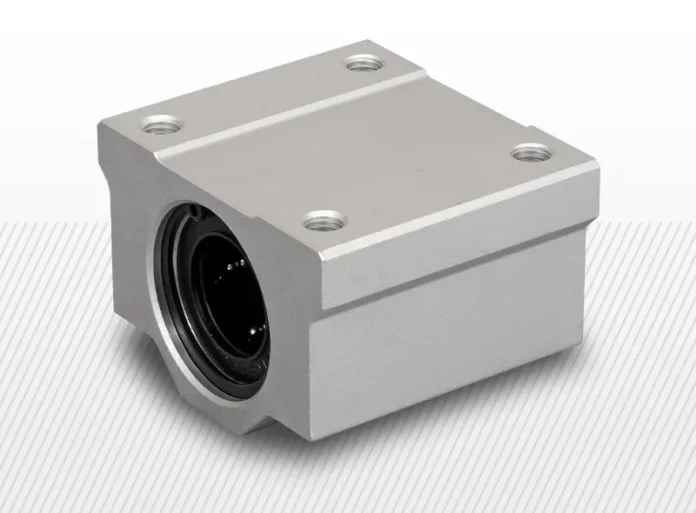

- Linear bearings, known as recirculating ball bushings, are commonly used with hardened and ground shafts. These bearings have a small point contact area that minimizes rolling friction. However, they exert a high force on the shaft and should only be used on hardened shafts such as steel shafts (Cf53) or stainless steel shafts (X90CrMoV18). When it comes to low friction, Linear Bearings with balls can be grat option as shown here https://www.tuli-shop.com/linear-motion/ball-spindles/ball-screw-nuts .
- There is a type of system called Motion Guidance Systems, also known as ball guides and linear guideways. These systems use recirculating balls and run on a profiled rail that has a gothic arch-shaped ball groove, allowing for maximum load capacity. In order to prevent deformation from the highly loaded balls, the rail must be hardened. These systems are usually more tolerant of moments than traditional recirculating linear bearings.
2. Roller bearings

Compared to ball bearings of the same size, roller bearings have a higher basic load rating. However, they are not able to handle lateral forces as well. Typically, roller bearings are utilized as track rollers, but they can also be used in cross-roller guides.
- Track bearings are a type of bearing that rolls on its outer diameter along a corresponding track. They usually have rollers as their rolling element, but sometimes they may have balls to handle radial load capacity. There are many different styles of track bearings available. The simplest type is a heavy-duty full complement roller bearing, such as NUTR. Other styles have profiled outer rings that are either v-shaped or concave to match a shaped and sometimes hardened rail. They can be attached using spigots, threaded studs, or weldable hubs. Some designs incorporate a secondary axial roller to handle lateral loads, known as combined roller bearings.
- Roller guides have a higher load capacity than ball guides of the same size. Even though they are small and precise, they are commonly used in medical applications.
- Cross-roller slides are known for their high accuracy and load capacities, but their design makes them susceptible to contamination. As a result, they are mainly used in clean rooms or vacuum environments.
3. Plain bearings
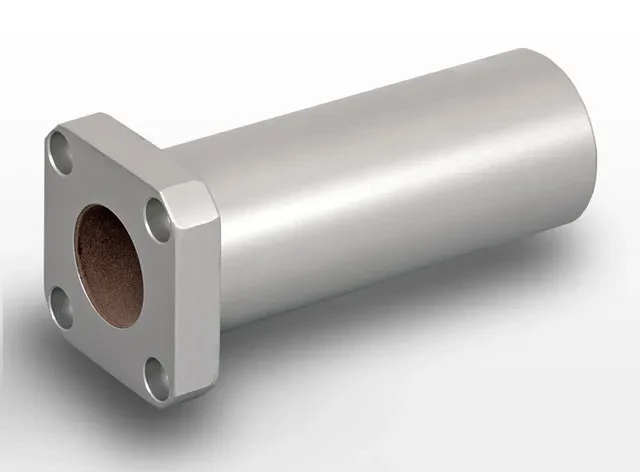

Over the past two decades, there has been significant progress in the development of low-friction plastics for plain bearings (also known as bushes). These bearings are mostly made from either plastic or ceramic materials. Although they offer reduced friction, their coefficient of friction is typically much higher compared to rolling element bearings.
- Linear bearings made of plastic are cost-effective and provide lower friction compared to using two similar materials. Since they don’t have rolling parts, there is less chance of product contamination due to dirt, dust, and debris, and they operate quietly. Nowadays, there are various types of plastic bearings available, each with its own unique advantages.
- Linear bearings made of ceramic share many similarities with those made of plastic. They have a quiet and smooth operation, come in the same sizes as standard recirculating linear bearings, and can even function without lubrication. Additionally, some types of ceramic linear bearings allow for both linear and rotational motion.
Tips to choose the right products – factors to consider
When choosing linear motion products, there are various factors to keep in mind. The market offers a wide range of products in different shapes and sizes. While cost is important, it’s crucial to consider the strengths and weaknesses of each system during the design process.
Factors to consider include:
When selecting a linear motion system, there are several factors to consider. These include load capacity, precision, support arrangement, environment, corrosion resistance, size and scale, and friction.
Depending on your specific needs, you’ll need to determine whether moments are involved in the load capacity, the level of precision required (you want to find some profiles that can be precisely cut, such as aluminium profile 80×80 by Tuli), the type of support arrangement needed (fully supported, end supported, cantilevered, or telescopic), the environment the system will be used in (dirty/dusty, clean room, vacuum, or outside), the level of corrosion resistance needed (for medical, pharmaceutical, or food industries), the size and scale of the system (whether compact, heavy-duty, or somewhere in between), and the level of friction with regards to the drive system.